
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Others
- Links between Thyroid Disorders and Glucose Homeostasis
- Young Sil Eom, Jessica R. Wilson, Victor J. Bernet
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):239-256. Published online March 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0013
- 11,003 View
- 636 Download
- 23 Web of Science
- 21 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Thyroid disorders and diabetes mellitus often coexist and are closely related. Several studies have shown a higher prevalence of thyroid disorders in patients with diabetes mellitus and vice versa. Thyroid hormone affects glucose homeostasis by impacting pancreatic β-cell development and glucose metabolism through several organs such as the liver, gastrointestinal tract, pancreas, adipose tissue, skeletal muscles, and the central nervous system. The present review discusses the effect of thyroid hormone on glucose homeostasis. We also review the relationship between thyroid disease and diabetes mellitus: type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes, as well as guidelines for screening thyroid function with each disorder. Finally, we provide an overview of the effects of antidiabetic drugs on thyroid hormone and thyroid disorders.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Linkage and association of rs3110045 and rs28499085 variants in the thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor (TRHR) gene with the risk of familial type 2 diabetes
Rongling Wu, Claudia Gragnoli
Aspects of Molecular Medicine.2024; 3: 100037. CrossRef - Obesity and Obesity-Related Thyroid Dysfunction: Any Potential Role for the Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD)?
Sebastián Pablo Chapela, Alison Simancas-Racines, Florencia Ceriani, Andrés Luciano Nicolas Martinuzzi, María Paula Russo, Ana Karina Zambrano, Daniel Simancas-Racines, Ludovica Verde, Giovanna Muscogiuri, Christos S. Katsanos, Evelyn Frias-Toral, Luigi B
Current Nutrition Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - View on Metformin: Antidiabetic and Pleiotropic Effects, Pharmacokinetics, Side Effects, and Sex-Related Differences
Guglielmina Froldi
Pharmaceuticals.2024; 17(4): 478. CrossRef - Thyroid Hormones and Diabetes in Euthyroid Hispanic/Latino Adults of Diverse Backgrounds: HCHS/SOL
Victoria Persky, Chibuzor Abasilim, Konstantina Tsintsifas, Tessa Day, Robert M Sargis, Martha Daviglus, Jianwen Cai, Sally Freels, Robert Kaplan, Carmen R Isasi, Amber Pirzada, Michelle L Meyer, Gregory A Talavera, Bharat Thyagarajan, Shivani Agarwal, No
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Managing Adults With Hypoglycemia
Christopher James Watson, Jonathan A. Edlow
Annals of Emergency Medicine.2023; 82(6): 705. CrossRef - Relationship of Glucose, C-peptide, Leptin, and BDNF in Maternal and Umbilical Vein Blood in Type-1 Diabetes
Josip Delmis, Slavko Oreskovic, Vesna Elvedji Gasparovic, Mirta Starcevic, Mislav Herman, Nada Dessardo, Vito Starcevic, Marina Ivanisevic
Nutrients.2023; 15(3): 600. CrossRef - Isolated Maternal Hypothyroxinemia May be Associated with Insulin
Requirement in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Ömercan Topaloğlu, Mehmet Uzun, Seda Nur Topaloğlu, Ibrahim Sahin
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2023; 55(04): 245. CrossRef - Association of urinary iodine concentration with prediabetes/diabetes in adults: Analysis of the NHANES 2005–2016
Jingmin Chen, Huanzhu Liang, Yuxuan Tan, Lin Wen, Ziang Guo, Jiyu Nie, Xiaoxiao Lin, Feng Huang, Jie Wang, Puyi Xing, Lihong Nie, Lihong Wang, Chunxia Jing
Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology.2023; 77: 127144. CrossRef - Central sensitivity to thyroid hormones is reduced in youths with overweight or obesity and impaired glucose tolerance
Procolo Di Bonito, Domenico Corica, Maria Rosaria Licenziati, Anna Di Sessa, Emanuele Miraglia del Giudice, Maria Felicia Faienza, Valeria Calcaterra, Francesca Franco, Giulio Maltoni, Giuliana Valerio, Malgorzata Wasniewska
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of thyroid stimulating hormone and time in range with risk of diabetic retinopathy in euthyroid type 2 diabetes
Yaxin Wang, Jingyi Lu, Jiaying Ni, Ming Wang, Yun Shen, Wei Lu, Wei Zhu, Yuqian Bao, Jian Zhou
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The circadian rhythm: an influential soundtrack in the diabetes story
Amirali Hariri, Mina Mirian, Ali Zarrabi, Mohammad Kohandel, Maryam Amini-Pozveh, Amir Reza Aref, Aliye Tabatabaee, Pranav Kumar Prabhakar, Ponnurengam Malliappan Sivakumar
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Folate deficiency may increase the risk for elevated TSH in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Lin Lin, Yushan Du, Guanyu Niu, Shuangbo Xia, Jufen Liu
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - L- Thyroxine ameliorates renal function in thyroidectomized diabetic nephropathy rats through downregulation of TGF- β1, Ang II and ET-1 expression
Zeinab H. El-Said, Sherihan I. Gouda, Hebatallah A. Mahgoub, S El_desouky, Neven A. Ebrahim
Egyptian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences.2023; 10(1): 632. CrossRef - Thyroid dysfunction in children and adolescents affected by undernourished and overnourished eating disorders
Valeria Calcaterra, Vittoria Carlotta Magenes, Francesca Siccardo, Chiara Hruby, Martina Basso, Veronica Conte, Giulia Maggioni, Valentina Fabiano, Susanna Russo, Pierangelo Veggiotti, Gianvincenzo Zuccotti
Frontiers in Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Preventive Effect of Molecular Iodine in Pancreatic Disorders from Hypothyroid Rabbits
Julia Rodríguez-Castelán, Evangelina Delgado-González, Esteban Rodríguez-Benítez, Francisco Castelán, Estela Cuevas-Romero, Brenda Anguiano, Michael C. Jeziorski, Carmen Aceves
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(19): 14903. CrossRef - Hypothyroidism increases angiotensinogen gene expression associated with vascular smooth muscle cells cholesterol metabolism dysfunction and aorta remodeling in Psammomys obesus
Samia Neggazi, Nadjiba Hamlat, Sihem Berdja, Saliha Boumaza, Leila Smail, Michel Beylot, Souhila Aouichat-Bouguerra
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Correlation Between Thyroid Parameters and the Ratios of Neutrophil/Lymphocyte and Platelet/Lymphocyte in Euthyroid Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Hui Chen, Jun-Qiang Ju, Xiao-Wu Qian, Zheng-Tai Zhu, Chun-Zhi Zhao, Zhe Liu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 3763. CrossRef - Effects of high-intensity interval training program on pituartry function in basketball players: a randomized controlled trial
Recep Soslu, Abdullah Uysal, Meltem Devrilmez, İsmail Can Çuvalcıoğlu, Ali Ahmet Doğan, Sülbiye Karaburgu, Murat Taş
Frontiers in Physiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Selenium and Selenoproteins at the Intersection of Type 2 Diabetes and Thyroid Pathophysiology
Francesca Gorini, Cristina Vassalle
Antioxidants.2022; 11(6): 1188. CrossRef - TSH levels within the normal range and risk of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality among individuals with diabetes
Ping Zhu, Guojuan Lao, Chuping Chen, Lihui Luo, Jing Gu, Jianmin Ran
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolite Changes during the Transition from Hyperthyroidism to Euthyroidism in Patients with Graves’ Disease
Ho Yeop Lee, Byeong Chang Sim, Ha Thi Nga, Ji Sun Moon, Jingwen Tian, Nguyen Thi Linh, Sang Hyeon Ju, Dong Wook Choi, Daiki Setoyama, Hyon-Seung Yi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 891. CrossRef
- Linkage and association of rs3110045 and rs28499085 variants in the thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor (TRHR) gene with the risk of familial type 2 diabetes
- Basic Research
- Notch1 Has an Important Role in β-Cell Mass Determination and Development of Diabetes
- Young Sil Eom, A-Ryeong Gwon, Kyung Min Kwak, Jin-Young Youn, Heekyoung Park, Kwang-Won Kim, Byung-Joon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(1):86-96. Published online February 26, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0160
- 6,346 View
- 185 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
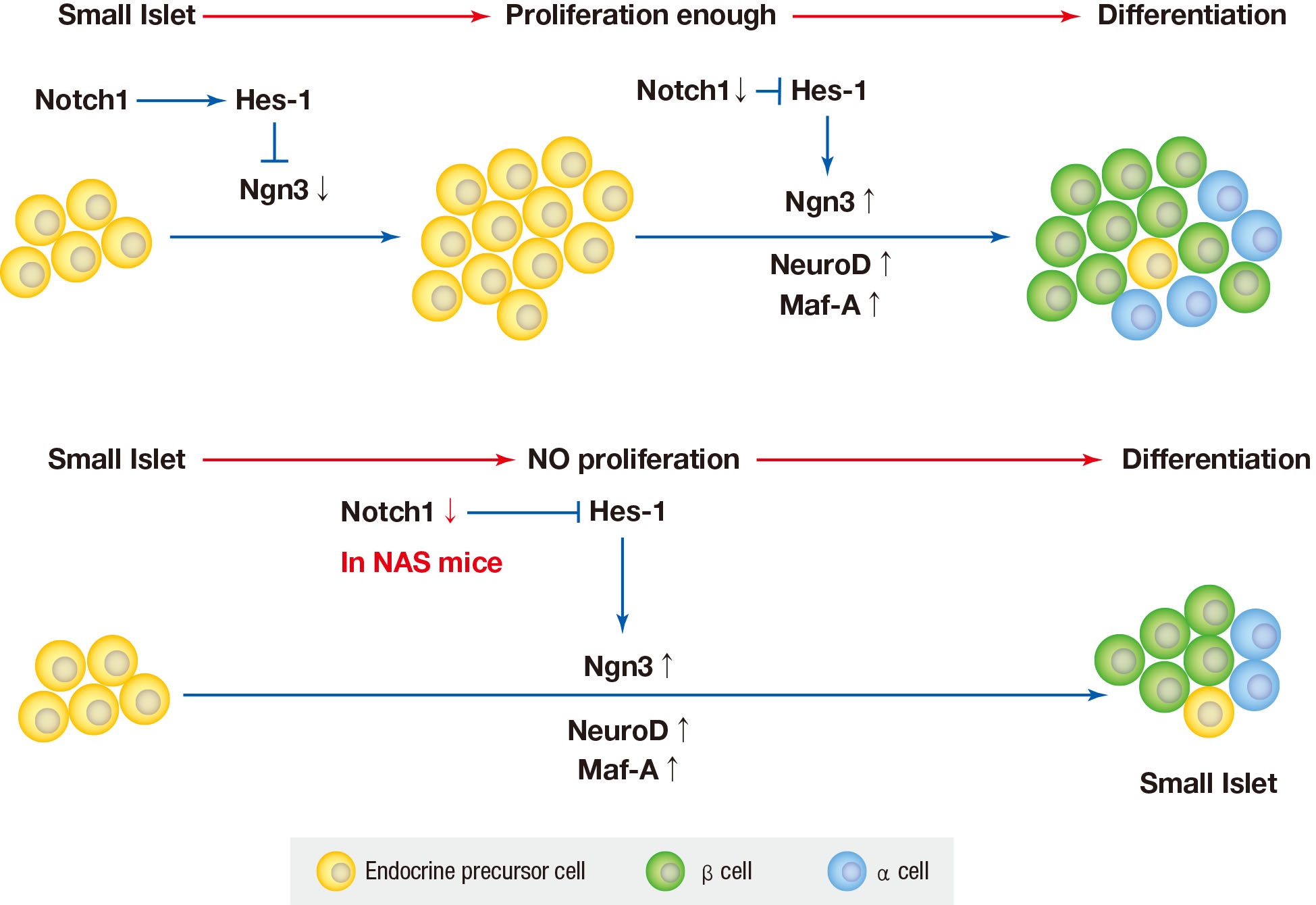
Background Notch signaling pathway plays an important role in regulating pancreatic endocrine and exocrine cell fate during pancreas development. Notch signaling is also expressed in adult pancreas. There are few studies on the effect of Notch on adult pancreas. Here, we investigated the role of Notch in islet mass and glucose homeostasis in adult pancreas using Notch1 antisense transgenic (NAS).
Methods Western blot analysis was performed for the liver of 8-week-old male NAS mice. We also conducted an intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (IPGTT) and intraperitoneal insulin tolerance test in 8-week-old male NAS mice and male C57BL/6 mice (control). Morphologic observation of pancreatic islet and β-cell was conducted in two groups. Insulin secretion capacity in islets was measured by glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) and perifusion.
Results NAS mice showed higher glucose levels and lower insulin secretion in IPGTT than the control mice. There was no significant difference in insulin resistance. Total islet and β-cell masses were decreased in NAS mice. The number of large islets (≥250 µm) decreased while that of small islets (<250 µm) increased. Reduced insulin secretion was observed in GSIS and perifusion. Neurogenin3, neurogenic differentiation, and MAF bZIP transcription factor A levels increased in NAS mice.
Conclusion Our study provides that Notch1 inhibition decreased insulin secretion and decreased islet and β-cell masses. It is thought that Notch1 inhibition suppresses islet proliferation and induces differentiation of small islets. In conclusion, Notch signaling pathway may play an important role in β-cell mass determination and diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- N6-methylation of RNA-bound adenosine regulator HNRNPC promotes vascular endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus by activating the PSEN1-mediated Notch pathway
Ying Cai, Tao Chen, Mingzhu Wang, Lihua Deng, Cui Li, Siqian Fu, Kangling Xie
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 197: 110261. CrossRef - Single‐cell RNA sequencing: Inhibited Notch2 signalling underlying the increased lens fibre cells differentiation in high myopia
Yunqian Yao, Ling Wei, Zhenhua Chen, Hao Li, Jiao Qi, Qingfeng Wu, Xingtao Zhou, Yi Lu, Xiangjia Zhu
Cell Proliferation.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro ribonucleic acid‐363 regulates the phosphatidylinositol 3‐kinase/threonine protein kinase axis by targeting NOTCH1 and forkhead box C2, leading to hepatic glucose and lipids metabolism disorder in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Yu‐Huan Peng, Ping Wang, Xiao‐Qun He, Ming‐Zhao Hong, Feng Liu
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(2): 236. CrossRef - Soluble T-cadherin promotes pancreatic β-cell proliferation by upregulating Notch signaling
Tomonori Okita, Shunbun Kita, Shiro Fukuda, Keita Fukuoka, Emi Kawada-Horitani, Masahito Iioka, Yuto Nakamura, Yuya Fujishima, Hitoshi Nishizawa, Dan Kawamori, Taka-aki Matsuoka, Maeda Norikazu, Iichiro Shimomura
iScience.2022; 25(11): 105404. CrossRef - Comparison of islet isolation result and clinical applicability according to GMP‐grade collagenase enzyme blend in adult porcine islet isolation and culture
Kyungmin Kwak, Jae‐kyung Park, Joohyun Shim, Nayoung Ko, Hyoung‐Joo Kim, Yongjin Lee, Jun‐Hyeong Kim, Michael Alexander, Jonathan R. T. Lakey, Hyunil Kim, Kimyung Choi
Xenotransplantation.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Genome-Wide Meta-analysis Identifies Genetic Variants Associated With Glycemic Response to Sulfonylureas
Adem Y. Dawed, Sook Wah Yee, Kaixin Zhou, Nienke van Leeuwen, Yanfei Zhang, Moneeza K. Siddiqui, Amy Etheridge, Federico Innocenti, Fei Xu, Josephine H. Li, Joline W. Beulens, Amber A. van der Heijden, Roderick C. Slieker, Yu-Chuan Chang, Josep M. Mercade
Diabetes Care.2021; 44(12): 2673. CrossRef
- N6-methylation of RNA-bound adenosine regulator HNRNPC promotes vascular endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus by activating the PSEN1-mediated Notch pathway
- Evaluation of Stress in Korean Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Using the Problem Areas in Diabetes-Korea Questionnaire
- Young Sil Eom, Hwa Sun Park, Sei-Hyun Kim, Sun Mee Yang, Moon Suk Nam, Hyoung Woo Lee, Ki Young Lee, Sihoon Lee, Yeun Sun Kim, Ie Byung Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(2):182-187. Published online April 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.2.182
- 4,441 View
- 56 Download
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background It is known that diabetes and stress are directly or indirectly related, and that it is important to evaluate stress in patients with diabetes. The relationship between Korean diabetics and diabetes-related stress has never been reported. The objective of this study was to develop a stress questionnaire suitable for use with Korean diabetics and to evaluate its utility.
Methods This study subjects were 307 Korean diabetics, aged 40 to 74 years old, who visited the Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism at Gachon University Gil Hospital, Yeungnam University Medical Center, and Inha University Hospital in Korea between March 2006 and February 2008. We developed a Korean version of Polonsky's Problem Areas in Diabetes (PAID) stress questionnaire (PAID-K) and used it to assess degrees of stress in our sample of Korean patients. We evaluated the utility of the questionnaire and analyzed the relationships between clinical characteristics of the study subjects and degrees of stress.
Results Cronbach's alpha for PAID-K was 0.95, and PAID-K scores were significantly correlated with Hypoglycemia Fear Survey scores (
r =0.44,P <0.05) and State Trait Anxiety Inventory-6 scores (r =0.21,P <0.05). PAID-K scores were significantly higher in patients with longer durations of diabetes, patients using insulin, and female patients (P =0.02,P =0.038, andP =0.001, respectively). The score also tended to increase as HbA1c levels increased, except for very high HbA1c levels (above 11%) (P for trend<0.05).Conclusion We developed the PAID-K questionnaire and demonstrated its utility to evaluate levels of stress in diabetic patients in Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of diabetes distress on glycemic control and diabetic complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Hye-Sun Park, Yongin Cho, Da Hea Seo, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongbin Hong, Young Ju Suh, Suk Chon, Jeong-Taek Woo, Sei Hyun Baik, Kwan Woo Lee, So Hun Kim
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Distress Measurement Related to Glucose Monitoring of Diabetes Patients
Eujin Choi, Sooyeon Kim, Juhee Cho, Min-Sun Kim, Eun Kyung Kwon, Youngha Kim, Danbee Kang, Sung Yoon Cho
Diabetes Therapy.2023; 14(4): 737. CrossRef - Development and validation of a distress measurement for insulin injections among patients with diabetes
Eujin Choi, Min-Sun Kim, Juhee Cho, Sooyeon Kim, Eun Kyung Kwon, Youngha Kim, Danbee Kang, Sung Yoon Cho
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Experiential Avoidance on the Relationship between Diabetes Distress and Self-Stigma in People with Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 in Republic of Korea
Kawoun Seo
Healthcare.2023; 11(20): 2773. CrossRef - Patient-reported outcome measures for assessing health-related quality of life in people with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review
Marlous Langendoen-Gort, Lenka Groeneveld, Cecilia A. C. Prinsen, Joline W. Beulens, Petra J. M. Elders, Ilana Halperin, Geetha Mukerji, Caroline B. Terwee, Femke Rutters
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2022; 23(5): 931. CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Acceptance Action in the Relationship between Diabetes Distress and Self-stigma among Old Adults with Diabetes in South Korea
Hyesun Kim, Kawoun Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2022; 33(4): 446. CrossRef - Mobile Healthcare System Provided by Primary Care Physicians Improves Quality of Diabetes Care
Tae Jung Oh, Jie-Eun Lee, Seok Kim, Sooyoung Yoo, Hak Chul Jang
CardioMetabolic Syndrome Journal.2021; 1(1): 88. CrossRef - Measurement Properties of Patient-Reported Outcome Measures for Diabetes: Systematic Review
Priscilla Jia Ling Wee, Yu Heng Kwan, Dionne Hui Fang Loh, Jie Kie Phang, Troy H Puar, Truls Østbye, Julian Thumboo, Sungwon Yoon, Lian Leng Low
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2021; 23(8): e25002. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Acceptance and Action Questionnaire-Stigma (AAQ-S-K)
Hyunjin Lee, Myoungjin Kwon, Kawoun Seo
Healthcare.2021; 9(10): 1355. CrossRef - Adherence to Mediterranean diet and advanced glycation endproducts in patients with diabetes
Marko Grahovac, Marko Kumric, Marino Vilovic, Dinko Martinovic, Ante Kreso, Tina Ticinovic Kurir, Josip Vrdoljak, Karlo Prizmic, Joško Božić
World Journal of Diabetes.2021; 12(11): 1942. CrossRef - The Impact of a Community-Based Food Education Program on Nutrition-Related Knowledge in Middle-Aged and Older Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Results of a Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
Carlos Vasconcelos, António Almeida, Maria Cabral, Elisabete Ramos, Romeu Mendes
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 16(13): 2403. CrossRef - The Effects of the 2030 Diabetes Camp Program on Depression, Anxiety, and Stress in Diabetic Patients
Jin Hee Jung, Jung Hwa Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2019; 20(3): 194. CrossRef - Research of Type 2 Diabetes Patients’ Problem Areas and Affecting Factors
Sebahat Atalikoğlu Başkan, Mehtap Tan
Journal of Diabetes Mellitus.2017; 07(03): 175. CrossRef - Diabetes-related emotional distress instruments: A systematic review of measurement properties
Jiyeon Lee, Eun-Hyun Lee, Chun-Ja Kim, Seung Hei Moon
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2015; 52(12): 1868. CrossRef - Internet-Based Mentoring Program for Patients with Type 1 Diabetes
Sun-Hye Ko, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(2): 107. CrossRef - Influence of the Duration of Diabetes on the Outcome of a Diabetes Self-Management Education Program
Seung-Hyun Ko, Sin-Ae Park, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Sun-Hye Ko, Kyung-Mi Shin, Seung-Hwan Lee, Ki-Ho Song, Yong-Moon Park, Yu-Bae Ahn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2012; 36(3): 222. CrossRef
- Impact of diabetes distress on glycemic control and diabetic complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Association of Educational Level and Socioeconomic Status with Glucose Metabolism.
- Young Sil Eom, Sun Mee Yang, Pyung Chun Oh, Jung Hyun Lee, Ki Young Lee, Yeun Sun Kim, Sihoon Lee, Jung Soo Im, Jun Yim, Dae Kyu Oh, Moon Suk Nam, Ie Byung Park
- Korean Diabetes J. 2008;32(4):377-385. Published online August 1, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2008.32.4.377
- 2,314 View
- 26 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The objective of the present study was to examine the association of educational level and socioeconomic status with glucose metabolism including prediabetes. METHODS: This cross-sectional study subjects were 882 (mean age: 51.0 +/- 13.4 years, M:F = 241:641) without diabetes, aged more than 20 years and residing in Whasu 2 dong in Incheon. We classified them into three levels according to their educational level: primary (illiterate or up to elementary school), secondary (middle school or high school) and tertiary (university), and into three levels according to their socioeconomic status by self reported questionnaire: low, middle and high. Subjects were diagnosed as three groups (normal, prediabetes and diabetes) by American Diabetes Association criteria using 75 g oral glucose tolerance test. The association of educational level and socioeconomic status with glucose metabolism was analyzed. RESULTS: The number of normal group was 300 (34.0%), that of prediabetes was 470 (53.3%) and that of diabetes was 112 (12.7%). In women, the proportion of primary educational group was larger than that of secondary educational group in diabetes (Odds ratio [OR] = 1.88; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.01-3.51) and larger than that of tertiary educational group in prediabetes ([OR] = 2.00; [CI]: 1.06-3.78). But socioeconomic status did not have the statistical association with glucose metabolism in women. Also both educational level and socioeconomic status had no statistical association with glucose metabolism in men. CONCLUSIONS: The proportion of low educational level is larger in prediabetes and diabetes compared with normal group in women. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How do life-course trajectories of socioeconomic position affect quality of life in patients with diabetes mellitus?
Hye Ah Lee, Ko Eun Lee, Yool Won Jeong, Jaeseon Ryu, Minkyung Kim, Jung Won Min, Young Sun Hong, Kyunghee Jung-Choi, Hyesook Park
Quality of Life Research.2014; 23(4): 1337. CrossRef
- How do life-course trajectories of socioeconomic position affect quality of life in patients with diabetes mellitus?

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





